Recently, teacher Zhu Jianyue from the communication network and testing technology team of our college, as the first author, published a research paper titled "Joint Optimization of User Scheduling, Rate Allocation, and Beamforming for RSMA Finite Blocklength Transmission" in "IEEE Internet of Things Journal" (SCI Zone 1, high-quality T1 journal, impact factor 10.6). Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology is the first unit, and teacher Zhu Jianyue is the first author and corresponding author.
With the rapid development of 6G wireless networks, especially in application scenarios such as enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC), communication technology is facing stringent requirements for higher data rates, extremely low latency, and higher reliability. Rate-Splitting Multiple Access (RSMA) technology has become one of the key technologies of 6G systems due to its significant advantages in spectral efficiency, energy efficiency, quality of service, and user fairness in multi-user multi-antenna communication networks. However, most existing RSMA technology research is based on the assumption of infinite blocklength transmission. Although this assumption simplifies the problem in theoretical analysis, it is quite different from the actual data transmission method. Therefore, the research on finite blocklength transmission is particularly important. This study introduces RSMA technology into the finite blocklength transmission scenario for the first time and proposes a joint optimization scheme of user scheduling, rate allocation, and beamforming. By designing an algorithm based on alternating optimization and combining techniques such as strong Lagrangian duality method and convex function difference programming, the complex optimization problem is successfully solved. Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, providing valuable references and inspirations for the further development of 6G wireless networks.
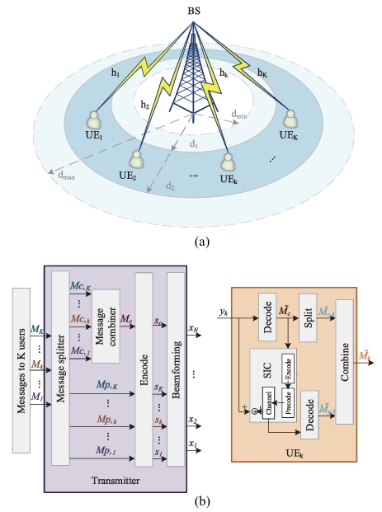
Figure 1. Description of MISO RSMA FBL transmission link: (a) User distribution (b) RSMA transceiver architecture.
The link of the article:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10591333
